What is Google Page Speed and how to improve it?
Posted By: Akanksha mall Published: 24, Mar 2025
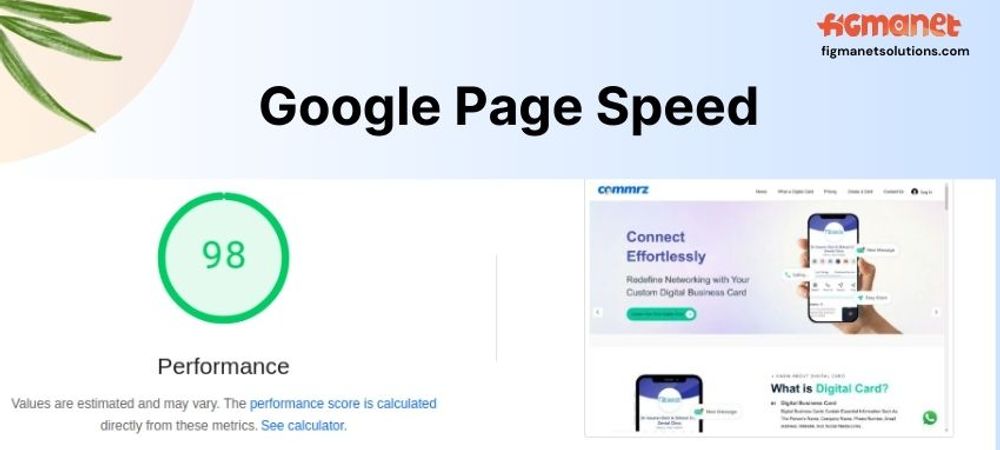
A Comprehensive Guide to Google Page Speed
In today’s digital landscape, website speed is crucial. A slow-loading site not only frustrates users but also negatively impacts your search engine rankings. Google Page Speed is a vital tool that measures the performance of your website and provides insights on how to improve loading times. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the importance of Google Page Speed, how to assess your site’s performance, and strategies to enhance speed for a better user experience.
Why Google Page Speed Matters
-
User Experience: Studies have shown that users tend to abandon websites that take longer than 3 seconds to load. A faster website means happier users and a lower bounce rate.
-
SEO Rankings: Google has made it clear that page speed is a ranking factor. Sites that load quickly are more likely to rank higher in search engine results.
-
Conversion Rates: Speed impacts conversion rates; faster-loading pages tend to convert visitors into customers more effectively.
-
Mobile Experience: With the increasing use of mobile devices, optimizing page speed for mobile users is critical. The Google Page Speed Insights tool provides specific recommendations for mobile optimization.
Assessing Your Website’s Performance
To get started, use Google PageSpeed Insights. This free tool analyzes your website and provides a score ranging from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better performance. It grades both mobile and desktop versions of your site and offers actionable recommendations for improvement.
Key Metrics:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): FCP stands for First Contentful Paint, a crucial performance metric in web development that measures the time it takes for the first piece of content (like text, images, or canvas elements) to be rendered on the screen after a user navigates to a web page. This metric helps developers understand how quickly users can perceive that the page is loading and becoming interactive.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): LCP stands for Largest Contentful Paint, a critical performance metric that measures how long it takes for the largest piece of content on a webpage to become visible within the viewport. This content could be an image, a video, a large block of text, or any other significant element that conveys important information to users.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS stands for Cumulative Layout Shift, a performance metric that measures the visual stability of a webpage. It quantifies how much the layout of a webpage shifts unexpectedly during loading. CLS is part of Google’s Core Web Vitals, which are essential for assessing the user experience on websites.
By understanding these metrics, you can pinpoint areas that require attention.
Tips for Improving Google Page Speed
-
Optimize Images: Large images can significantly slow down your site. Use formats like WebP for transparent backgrounds or JPEG for photos. Consider using responsive images that adapt to different screen sizes.
-
Minimize HTTP Requests: Each element on your page (images, CSS, JavaScript) requires an HTTP request. Reduce the number of elements or use techniques like CSS sprites to combine images.
-
Leverage Browser Caching: Enable caching to store frequently accessed resources in your users’ browsers. This reduces load time for repeat visitors.
-
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Remove unnecessary characters (like whitespace and comments) from your code. Minification reduces the size of your files, which speeds up loading times.
-
Lazy Loading: Lazy loading defers the loading of non-essential resources (such as images, videos, iframes, and even scripts) until they are required for display. This technique helps improve the performance of a web page, reduce initial load times, and conserve bandwidth.
-
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN distributes your content across multiple servers worldwide. This means your site loads faster for users, regardless of their location.
-
Asynchronous Loading for CSS and JavaScript: Instead of blocking page rendering, asynchronous loading allows files to load in the background. This improves perceived load times.
-
Reduce Redirects: Too many redirects create additional HTTP requests and delay page loading. Streamline your URLs to minimize redirects.
-
Choose a Reliable Hosting Provider: The quality of your hosting service can significantly impact your site’s speed. Invest in a reliable hosting provider that offers excellent performance.
Conclusion
In a world where speed matters, optimizing your website for Google Page Speed is essential for success. By regularly assessing your site’s performance and implementing best practices, you can enhance user experience, improve SEO rankings, and boost conversion rates. Remember, a faster website is not just a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity in today’s competitive online environment. Start optimizing today and watch your website performance soar!

